A business owner’s guide to the employment laws in Wisconsin

Navigating Wisconsin employment laws is crucial for maintaining a fair and compliant workplace. Both you and your employees benefit from understanding the rights and obligations, ensuring smoother operations and stronger professional relationships. A well-informed workplace not only reduces legal risks but also promotes transparency, trust, and a more engaged workforce.
In this blog, we will discuss Wisconsin labor laws, covering essential topics such as minimum wage, overtime, discrimination, harassment, and employee benefits. Finally, we will explore the potential consequences of non-compliance and introduce how Global Squirrels can help you overcome these challenges with our Purple plan.
What are some key Wisconsin labor laws?
Minimum wages & overtime pay
According to the Wisconsin labor laws, the minimum wage is $7.25 per hour and $5.90 per hour for opportunity employees (first 90 days of employment if under 20 years). Regardless of age, overtime pay at 1.5 times the regular hourly rate is required for any hours worked beyond 40 in a single workweek. Employers must maintain accurate records, comply with Wisconsin labor laws, and ensure fair compensation. While these laws differ from employment laws in Texas, the fundamental principles of fair pay and overtime compensation remain consistent. Being aware of these differences is imperative to businesses that are running across state lines in Wisconsin and Texas.
Work hours
Understanding work-hour regulations is crucial for both you and your employees to maintain compliance with Wisconsin labor laws. A standard workweek consisting of 40 hours and is scheduled within a calendar week or any regular recurring period of 168 hours consisting of seven consecutive 24-hour periods is a standard workweek in Wisconsin. The labor laws in this state are a part of the broader employment laws in the USA, emphasizing the importance of accurate record-keeping for work hours to ensure compliance. Workforce laws in Wisconsin also include specific regulations for minors under 18, such as limitations on night shifts and maximum hours during school days. While Wisconsin labor laws do not mandate meal or rest breaks for adult employees, employers are encouraged to provide reasonable breaks, and any breaks shorter than 30 minutes must be paid. Understanding these employment laws in Wisconsin helps businesses create a fair, compliant, and productive work environment.
Leaves
Work-life balance is essential to the State of Wisconsin, and it offers a range of leave options to its employees. Different types of leave are available as follows.
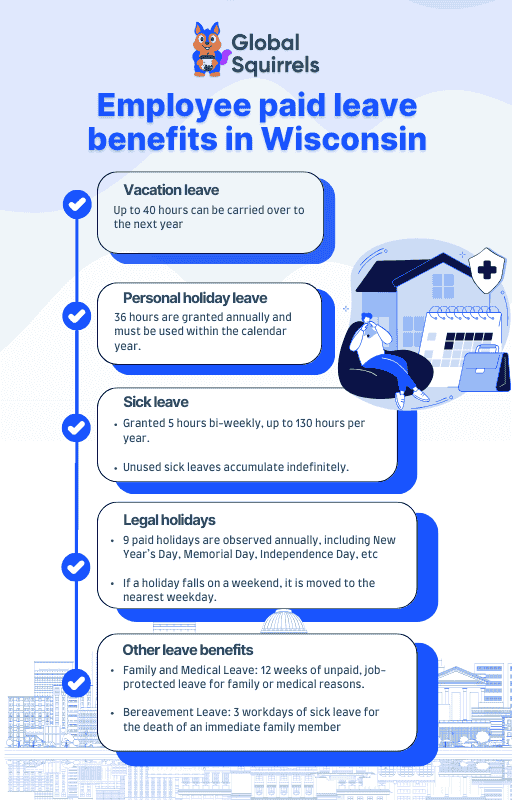
1. Vacation leave
Vacation hours are prorated for new employees in the first year, and they are able to use these hours after six months of probation (unclassified employees may use vacation immediately). At the start of each calendar year, vacation hours are granted, and up to 40 hours can be carried into the next year, but they must be used by June 30. Like vacation, employees are also eligible to cash out up to 40 hours of unused vacation or transfer hours to a sabbatical account. These provisions align with Wisconsin employment laws.
2. Personal Holiday Leave
Every year, employees are given personal holiday leave of 36 hours to use after a year of employment. However, these hours must be used during the calendar year, or they are forfeited. If an employee leaves or is fired within the first six months, he or she may need to return the hours used.
3. Sick Leave
Employees get up to 5 hours of sick leave per bi-weekly pay period and a maximum of 130 hours per year. Unused sick leave accumulates indefinitely and can be used later as health insurance credits when retiring. After 520 hours of sick leave, an employee is considered eligible to transfer unused vacation time into a sabbatical account. This is consistent with employment laws in Wisconsin.
4. Legal holidays
New Year’s Day, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving, and Christmas are nine paid legal holidays in Wisconsin. A holiday occurring on a weekend will adjust the day off to a nearby weekday.
5. Other leave benefits
- Exam/interview leave: Time off for exams and interviews related to state government jobs.
- Family and medical leave (FMLA and WFMLA): 12 weeks unpaid job-protected leave for specified family and medical reasons. Servicemember care is available in addition.
- Bereavement leave: Up to 3 workdays of sick leave for the death of an immediate family member, plus up to 4 additional days for travel if necessary.
Source link: dpm.wi.gov
Benefits
Wisconsin employment laws ensure state employees receive benefits packages covering health insurance, retirement, leave policies, insurance options, and financial programs.
1. Health, dental, and vision insurance
- State group health insurance: Provides hospital, surgical, medical, and prescription coverage. Employees can choose between a Standard Health Plan and a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) with an employer Health Savings Account (HSA) contribution.
- Dental insurance: Most State Group Health Insurance plans include basic preventive dental coverage, with supplemental dental plans available at the employee’s cost.
- Vision insurance: Covers eye exams, frames, lenses, and contact lenses. Optional vision care plans are available, with employees covering the full premium.
2. Retirement & savings programs
- Wisconsin retirement system (WRS): A mandatory pension plan where both employer and employee contribute 6.95% of covered earnings in 2025.
- Wisconsin deferred compensation (WDC): A voluntary retirement savings program that allows employees to make pre-tax or Roth contributions to supplement their retirement income.
- Pre-tax savings accounts:
- Healthcare flexible spending account (FSA): Annual contribution limit of $3,200.
- Dependent day care FSA: Annual contribution limit of $5,000.
- Health savings account (HSA): Employer contributes $828 (single) / $1,650 (family), with a total contribution limit of $4,300 (single) / $8,550 (family).
- Commuter benefits program: Allows employees to use pre-tax dollars for transit and parking expenses.
3. Leave benefits
- Vacation leave: Earned based on years of service (104-216 hours annually). Employees may use vacation leave after six months of service.
- Personal holiday: Employees receive 36 hours of paid personal holiday leave per year, which is available immediately.
- Legal holidays: Wisconsin employees receive 9 paid holidays, including New Year’s Day, Martin Luther King Jr. Day, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving, Christmas, and New Year’s Eve.
- Sick leave: Accrues at 5 hours per biweekly pay period (up to 130 hours per year). Unused sick leave can be converted into health insurance payments upon retirement.
- Family & medical leave: Workforce laws in Wisconsin require employers with 50 or more employees to provide six weeks of unpaid leave for birth or adoption.
4. Life, accident & disability insurance
- State group life insurance: Provides coverage up to five times the employee’s annual salary. Employees may also elect to cover spouses and dependents.
- Accident plan: Provides lump sum benefits for injuries, hospital stays, and accidental death.
- Income continuation insurance (ICI): Covers up to 75% of an employee’s salary if they are unable to work for at least 30 days due to illness or injury.
5. Employee assistance & wellness programs
- Employee assistance program (EAP): Offers free resources for work-life balance, financial and legal support, and mental health counseling.
- Wellness Wisconsin program: Provides a $150 wellness incentive for employees and spouses who complete a health check and well-being activity.
Simplified workforce management in Wisconsin
Stay compliant with Wisconsin employment laws effortlessly. Let Global Squirrels handle your payroll, benefits, and HR tasks while you focus on growing your business.
Request a demoDiscrimination and harassment laws in Wisconsin
Wisconsin employment laws protect employees from workplace discrimination and harassment based on ancestry, age (40 and older), arrest or conviction record, color, creed, disability, marital status, military reserve status, national origin, race, sex, and sexual orientation, with a 300-day statute of limitations to file a complaint.
Wisconsin labor laws prohibit employers, employment agencies, labor unions, and licensing agencies from making adverse employment decisions, such as hiring, firing, promotions, pay, benefits, job assignments, and training, based on these protected characteristics.
Employment laws in Wisconsin explicitly ban sexual harassment, including quid pro quo and hostile work environment harassment, as well as pregnancy discrimination and unfair treatment of individuals with disabilities, who are entitled to reasonable accommodations unless they pose an undue hardship.
Additionally, workforce laws in Wisconsin mandate that workplaces with 50 or more permanent employees provide up to six weeks of family leave for childbirth or adoption, ensuring parents have time to care for their children. Wisconsin also protects against perceived discrimination, such as assumptions about sexual orientation, and prohibits pre-employment inquiries that could reveal a candidate’s protected status. According to the Equal Rights Division, thousands of discrimination complaints are filed annually in Wisconsin, with disability and sex discrimination among the most common claims, highlighting the importance of enforcing Wisconsin labor laws to maintain fair and equitable workplaces.
What are the challenges of not complying with Wisconsin laws?
Non-compliance with Wisconsin laws, particularly in areas like income tax withholding, worker classification, and employment practices, can lead to significant challenges for businesses and individuals alike. Wisconsin employment laws mandate strict adherence to regulatory requirements to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability in the workplace. Failure to comply can result in financial penalties, legal actions, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
One major challenge is the financial burden of penalties and interest for late or incorrect filings. For instance, employers who fail to withhold or accurately report Wisconsin income taxes may face a penalty equal to the tax amount, plus interest and additional penalties. Misclassifying workers as independent contractors instead of employees can also trigger audits and result in substantial fines, including a $25,000 penalty for intentional misclassification in the construction industry. Additionally, businesses might incur costs associated with wage statement inaccuracies, delayed filings, and other reporting errors. Beyond the financial implications, non-compliance can tarnish an organization’s reputation, erode employee trust, and invite increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Adhering to employment laws in Wisconsin is crucial for you to avoid these pitfalls and maintain operational integrity.
How does Global Squirrels help eliminate all the challenges?
Global Squirrels is a staffing and payroll platform that helps you manage top talent effectively. Our platform helps your business with our Purple plan, which streamlines all essential HR functions, including payroll processing, timesheet management, benefits administration, task tracking, performance evaluation, and compliance with both state and federal labor and tax regulations through our Purple plan.
Navigating Wisconsin employment laws can be complex, but our Purple plan makes it simple by ensuring complete compliance with Wisconsin labor laws, helping you avoid risks such as worker misclassification and payroll inaccuracies. By utilizing state-specific tools like customizable timesheets, automated leave management, and real-time compliance monitoring, our platform helps you stay aligned with Wisconsin’s workforce regulations effortlessly.
Additionally, the Purple plan helps you manage payroll with precision, calculating wages, taxes, and statutory deductions while guaranteeing timely payments. With AI-powered features, tasks like generating offer letters, conducting compliance audits, and processing pay adjustments become quick and efficient. Our user-friendly dashboard also makes handling sensitive HR operations, such as promotions and terminations, straightforward and secure.
But what is the Purple plan?
The Purple plan is perfect for onboarding a pre-sourced candidate or converting an existing freelancer into a full-time employee. Simply log into our platform, select the Purple plan, and input the required candidate details—such as full name, email address, company-provided email, job title, responsibilities, start date, and any additional onboarding documents. Once initiated, Global Squirrels takes over the entire HR process, ensuring a smooth and compliant transition.
Struggling to stay compliant with Wisconsin labor laws? Let Global Squirrels handle the complexities. Request a demo today!