The ultimate guide to US minimum wage

Understanding the minimum wage in the United States is important for both employees and employers since it will directly impact compensation, economic policies, and business operations. While the federal government will set a baseline for minimum wage, individual states and cities have the power to set higher rates. This will often lead to varying pay standards across the country, thus creating confusion and complexities for businesses and workers alike.
In this guide, we have given in detail the history of minimum wage in America, its evolution over the years, and ongoing debates surrounding wage increases. We have also provided insights into state-specific laws, the impact of minimum wage on future trends, and multiple industries. Whether you are a business owner who is trying to ensure compliance with state and federal laws or an employee wanting to gain knowledge on rights and potential earnings, this guide will provide insights into all the important information you will require to understand all about the minimum wage in the USA.
What is the Federal US minimum wage?
The federal minimum wage in America is the lowest hourly pay rate that employers are legally required to pay their employees. It will act as the baseline wage, which applies across the country even though individual states and local governments have the authority to set higher minimum wage rates. The idea behind a federal minimum wage is to ensure that all workers are guaranteed a basic level of compensation for their labor, regardless of where they work within the country. As of 2025, the federal minimum wage remains set at $7.25 every hour. This means that employers will be legally required to pay their employees at least the given amount for every hour worked unless they are exempt or subject to certain state or local wage laws.
Exemptions and special cases:
While most workers are entitled to the federal minimum wage, there are certain exceptions:
1. Tipped employees
Workers who earn tips, such as servers and bartenders, can be paid a lower direct wage as long as their total earnings meet or can sometimes also exceed the federal minimum wage.
2. Youth workers
Employees under 20 years old can be paid a training wage of $4.25 every hour during the first 90 days of employment.
3. Certain disabled workers
Employers can pay individuals with disabilities a wage below the set federal minimum if approved under a special certificate from the Department of Labor.
To understand how federal wage policies align with broader employment regulations, explore our detailed guide on employment laws in the USA.
Minimum wage in America by state
The US minimum wage per hour varies across the country. While the federal government will set a baseline rate, every state will have the power to establish its own minimum wage laws, usually setting higher rates to reflect local economic conditions and the cost of living. This would mean that workers of one state might earn significantly more or less than those in another state, even if it’s for the same job.
Given below is the table that lists all the minimum wages across the top states that job seekers prefer working in, thus examining how minimum wage in America varies by region.
| State | 2025 Minimum Hourly Wage |
|
Alabama |
$7.25 |
|
Alaska |
$13.00 |
| California |
$16.50 |
|
Colorado |
$14.81 |
| Connecticut |
$16.35 |
|
Florida |
$13.00 |
| Georgia |
$7.25 |
|
Illinois |
$15.00 |
| Indiana |
$7.25 |
|
Kentucky |
$7.25 |
| Kansas |
$7.25 |
|
Maryland |
$15.00 |
| Massachusetts |
$15.00 |
|
Michigan |
$12.48 |
| Mississippi |
$7.25 |
|
New Jersey |
$15.49 |
| New York |
$16.50 |
|
North Carolina |
$7.25 |
| Ohio |
$10.70 |
|
Tennessee |
$7.25 |
| Texas |
$7.25 |
|
Washington, D.C. |
$17.95 |
| Wisconsin |
$7.25 |
Source: US Department of Labor
How often does the federal minimum wage increase?
The federal minimum wage in America is adjusted very rarely. However, the timing of this increase is driven by federal legislation rather than automatic adjustments based on cost-of-living or inflation. While the wage has been raised various times since its introduction in 1938, it has not been adjusted as frequently in the last few years. The federal minimum wage has remained at $7.25 per hour since July 24, 2009.
What triggers a federal minimum wage increase?
A rise in the minimum salary in the US per month will require action by the ruling party. Lawmakers should pass new legislation to change the wage, which is then signed into law by the President. This process can take years and is influenced by various factors. This includes:
1. Political landscape
Federal minimum wage increases usually depend on the political climate. Democratic administrations and legislators tend to support wage increases while Republicans are more likely to oppose them, citing concerns over business costs and job losses.
2. Economic conditions
Economic factors like inflation and unemployment rates will usually play a role in estimating whether the party will approve a minimum wage hike. During periods of economic downturn, lawmakers will be less inclined to increase wages because of fears of harming businesses or causing unemployment.
3. Public pressure and advocacy
Protests by labor unions, public campaigns, and worker advocacy groups can put pressure on lawmakers to increase the federal minimum wage. Media coverage, nationwide protests, and petitions have significantly helped in bringing attention to wage stagnation and pushing for legislative action.
4. State and local precedents
Sometimes, wages will increase at the state or city level, which creates momentum for federal action. When states like New York, California, or Washington raise their minimum wages significantly, it could influence federal discussions by highlighting the regional disparities and the need for a consistent baseline.
What is the impact of minimum wage on employees and employers?
The lowest minimum wage in the US will serve as a baseline for compensation in the labor market; however, its effects will extend beyond the paycheck. Understanding the impact on both employees and employers is important to evaluate the broader side of wage policies:
Impact on employees
1. Higher income and better standard of living
A higher minimum wage will directly increase earnings for low-wage workers, which will help them in meeting basic living expenses, reduce reliance on government assistance, and improve overall quality of life.
2. Increased productivity and job satisfaction
Employees earning a fair wage will often experience high morale and engagement, which will translate into improved productivity and lower the absenteeism rate.
3. Career motivation and skill development
A higher wage can motivate employees to upgrade their skills or pursue further training, thus contributing to career growth and long-term earning potential.
4. Reduced income inequality
By raising the floor for earnings, minimum wage laws will help in narrowing the gap between the low and middle-income earners, thus promoting a more equitable distribution of wealth.
5. Potential employment trade-offs
Certain studies suggest that a sudden or very large increase in minimum wage might lead to reduced hours or fewer entry-level positions, especially in small businesses or industries with thin profit margins.
Impact on employers
1. Higher labor costs
Increasing the minimum wage will raise payroll expenses, which will especially affect small businesses and labor-intensive industries like hospitality, food services, and retail.
2. Profit margins and price adjustments
To avail higher wages, certain businesses might increase product or service prices, which can impact competitiveness. Others might absorb the cost, thus reducing profit margins.
3. Employee recruitment and retention
Higher wages can improve employee retention by reducing training costs and turnover. It will also help in attracting a higher motivated and skilled workforce.
4. Operational adjustments
Employers might respond to higher wages by automating certain tasks, which will reduce staff hours or restructure roles to maintain efficiency while controlling costs.
5. Enhances brand image
Companies that pay fair wages can strengthen their brand reputation, which is usually appealing to socially conscious consumers and improves public perception.
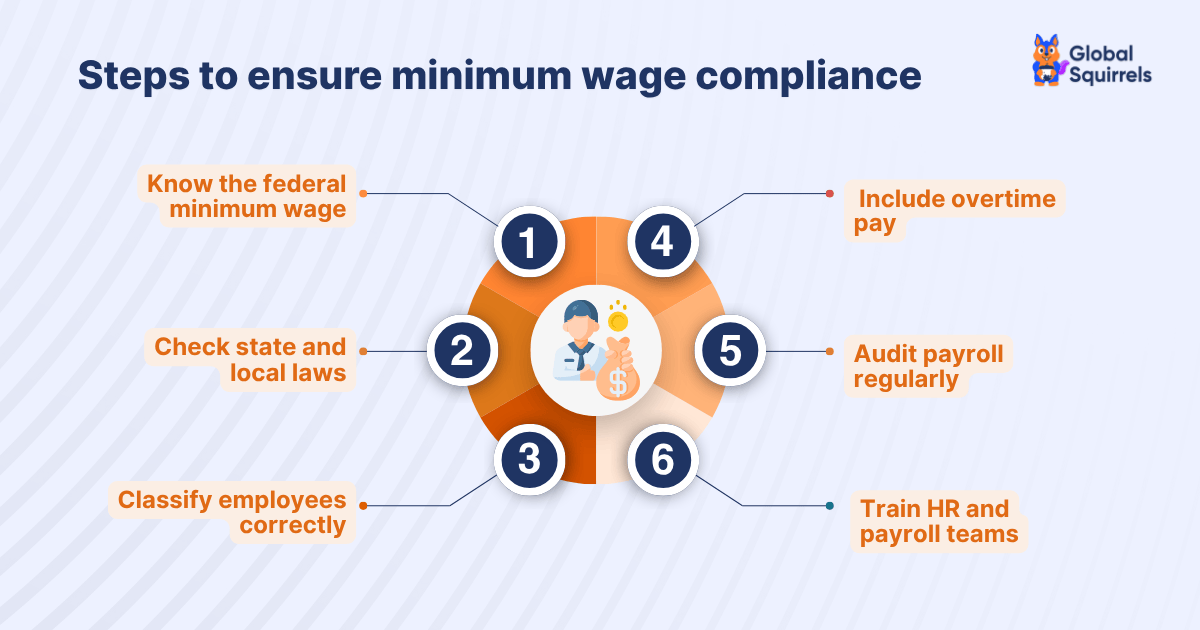
How will Global Squirrels help businesses navigate the US minimum wage laws?
Understanding and complying with US minimum wage laws will be challenging, especially for companies that are hiring across multiple states or managing remote teams. Global Squirrels is a staffing and payrolling platform that helps businesses hire, manage, and pay top local and remote talent. Regardless of the state from which you want to hire talent, our platform ensures 100% compliance with local laws, including the state’s minimum wage. Here’s how businesses in the USA leverage our staffing and EOR/payrolling platform:
1. Compliance with federal and state wage laws
Global Squirrels will ensure that your employees and contractors are being paid in accordance with federal, state, and local minimum wage regulations. Whether you are hiring in California or in Texas, where the federal rate applies, our platform will manage these differences automatically, thus reducing the risk of compliance violations and penalties.
2. Payroll management for employees
Managing payroll across multiple states with evolving minimum wages can get complicated and time-consuming. Global Squirrels will take care of accurate payroll processing, which includes deductions, taxes, and wage adjustments based on local laws, which will allow your HR and finance teams to focus on growth instead of administrative overhead.
3. Support for remote and contingent workers
For companies outsourcing contingent staff or remote teams, Global Squirrels will act as the Employer of Record (EOR). This means you can hire and manage workers without worrying about minimum wage compliance, benefits, or tax regulations in the US. This way, your global workforce will remain fully compliant and supported.
Check our Global Squirrels interactive demo to understand how our staffing and payrolling platform helps you manage US minimum wages across multiple states.
